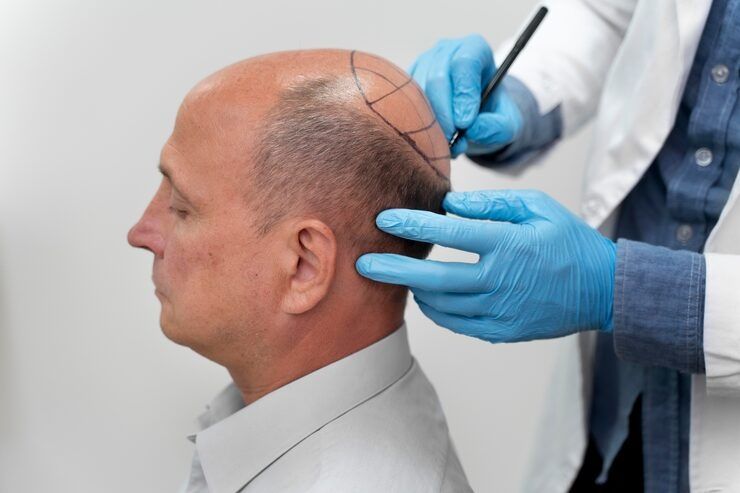
Hair transplants are a medical procedure designed to restore hair to areas of the scalp with thinning or no hair. They involve taking hair follicles from one part of the body—usually the back or sides of the scalp—and implanting them into the balding area. This technique has become a widely accepted solution for individuals facing hair loss due to genetics, aging, hormonal changes, or medical conditions.
The idea behind hair transplantation is not new. Since the 1950s, various methods have been developed, but modern advancements have significantly improved success rates, comfort, and appearance. Today, two primary methods are used: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). Each technique has its strengths and considerations, depending on individual needs and conditions.
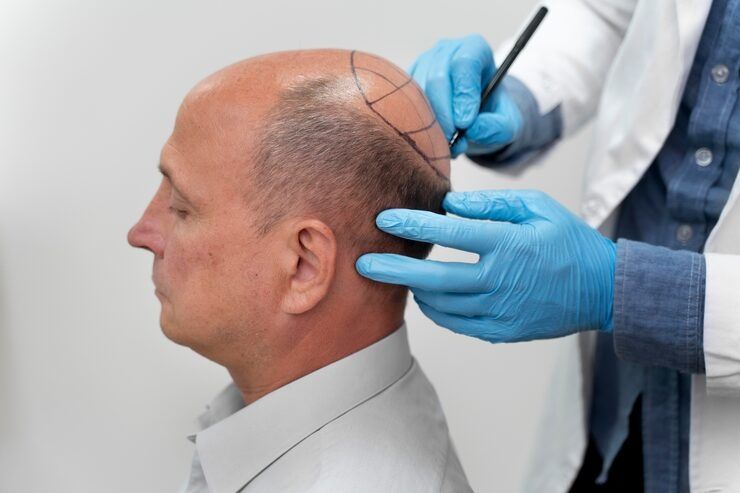
Hair transplants are not just about appearance—they can also positively impact a person's self-esteem, emotional well-being, and quality of life. As techniques become more refined and recovery times shorter, more people are exploring this option as a solution for long-term hair restoration.
Why Hair Transplants Matter Today
Hair loss affects millions of people worldwide, regardless of gender or age. According to the American Hair Loss Association, approximately two-thirds of men experience some degree of hair loss by age 35, and around 40% of hair loss sufferers are women.
This issue can impact self-image and confidence, especially in social or professional settings. While over-the-counter remedies and topical treatments exist, their effectiveness varies, and results may be temporary. Hair transplants, on the other hand, offer a more permanent solution.
Modern procedures have become less invasive and more precise, making them accessible to a broader audience. Medical tourism has also played a significant role in the popularity of hair transplants, with countries like Turkey, India, and Thailand offering quality procedures at competitive prices.
The demand for natural-looking results has led to significant advancements in both technology and technique. With increased awareness and reduced stigma, people now consider hair restoration not as vanity but as self-care.
Recent Trends and Developments (2024–2025)
The field of hair transplantation has evolved rapidly in the past year. One of the biggest trends in 2024 and continuing into 2025 is the use of robotic-assisted FUE techniques, such as ARTAS systems. These robots enhance precision and reduce recovery time.
Another notable trend is the integration of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy with hair transplants. PRP involves injecting a concentration of the patient’s own platelets to stimulate hair growth and improve graft survival rates.
Data from ISHRS (International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery) 2024 shows:
| Year | Global Hair Transplant Procedures | Average Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 735,000 | $4,000–$10,000 |
| 2024 | 850,000+ | $4,500–$12,000 |
In addition to techniques and outcomes, the diversity of patients has increased. More women and individuals with Afro-textured hair are seeking procedures tailored to their specific needs, prompting clinics to adopt more inclusive strategies.
Furthermore, clinics are now offering virtual consultations and using AI imaging to show potential results before committing to surgery, making the process more transparent and personalized.
Legal Considerations and Medical Regulations
Hair transplants are considered elective surgical procedures and are regulated differently depending on the country.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not regulate the transplant procedure itself but oversees the medical devices used during the process. Board-certified dermatologists or plastic surgeons typically perform the procedure, and clinics must follow strict hygiene and safety protocols.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and local health authorities regulate surgical procedures and ensure that facilities meet high standards. Similarly, India has guidelines from the Medical Council of India, and Turkey, a popular hub for hair transplants, requires clinics to be licensed and operate under medical supervision.
Patients are encouraged to verify a clinic’s accreditation, the doctor’s certifications, and patient reviews before proceeding. It's also important to know that in most countries, hair transplants are not covered by public health insurance, as they are classified as cosmetic treatments.
Regulatory authorities worldwide are increasing focus on preventing illegal clinics, unqualified practitioners, and misleading advertising. Always choose facilities that follow local medical laws and informed consent practices.
Helpful Tools and Resources
If you’re considering a hair transplant, several tools and resources can help you make informed decisions:
-
Hair Transplant Cost Calculators – Websites like RealSelf or WhatClinic provide cost comparisons based on country and technique.
-
Virtual Consultation Platforms – Some clinics offer AI-based apps to visualize results or provide a consultation remotely.
-
Accreditation Databases – Check surgeon credentials through ISHRS, ABHRS (American Board of Hair Restoration Surgery), or your country’s medical board.
-
Recovery Tracker Apps – Tools like PostOp or MyRecovery help monitor healing progress with daily photo uploads and alerts.
-
Educational Platforms – The ISHRS website offers guides, glossary terms, and before/after galleries to educate patients on expectations.
These tools can help reduce the uncertainty around procedures and allow users to ask better-informed questions during consultations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is a hair transplant permanent?
Yes, in most cases. Transplanted hair follicles are taken from areas resistant to hair loss and typically continue to grow for a lifetime. However, results can vary, and some people may need touch-ups over time.
Does the procedure hurt?
The process is usually performed under local anesthesia, so patients remain awake but experience minimal discomfort. Mild soreness or swelling may occur during the recovery phase.
How long does recovery take?
Most people can return to work within 3–5 days. Full recovery, including hair regrowth, can take 6–12 months. Proper post-care improves results and reduces the risk of complications.
Can women get hair transplants?
Yes. While most common in men, hair transplants are increasingly performed on women with thinning hair or traction alopecia. The approach may vary based on hair density and pattern.
Are there risks involved?
Like any surgical procedure, risks include infection, scarring, poor graft growth, or unnatural appearance. Choosing an experienced, certified surgeon significantly reduces these risks.
Conclusion
Hair transplants have become a reliable, medically supervised option for people experiencing hair loss. The combination of evolving techniques, better tools, and more transparency has made it easier than ever to explore this treatment confidently.
Understanding the procedure, legal aspects, and available resources can help you make informed choices that align with your health goals. Whether you're seeking to regain confidence or just explore your options, a well-researched approach is the best first step in your hair restoration journey.